What Is Radon and Why Should I Test For It?
Radon gas is found everywhere but is particularly high in our area. Radon is a naturally occurring decay product of the breakdown of the Uranium atom, hundreds of feet below the soil.

Radon Concentrations Across The State of TN
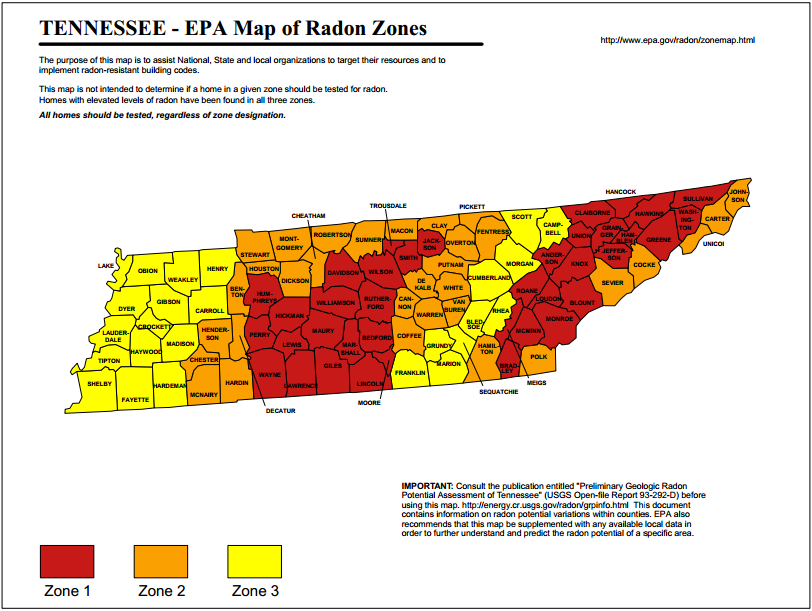
In NE Tennessee; Sullivan, Washington, Greene, and Hawkins counties are in Zone 1. This zone has an indoor testing average greater than 4.0 pci/l. While Carter and Unicoi Counties are in Zone 2, with an average between 2 – 4 pci/l.
Information on Testing
I test for the presence of Radon with the newest and most advanced monitor available on the market; the Corentium Pro. This monitor is fully AARST-NRPP certified, and uses a passive diffusion chamber, using alpha spectrometry to precisely calculate the radon level.
The monitor is set up on the lowest, lived-in level of the home, and runs for 48 hours. The monitors collects an hour by hour average of the radon concentration level in the home. The 48 hour average of the hour by hour readings, will be presented in the report that is produced.

This monitor also collects hour by hour temperature, humidity, and barometric pressure readings, as well as monitoring for movement or vibrations to the device. These temperature, humidity, pressure, and vibration readings are collected to alert us to the possibility that the test was tampered with. For example; someone trying to move the device outdoors, opening windows or doors, etc.
The test results are available immediately after collecting the device, and a full report showing all the data for 48 hours, is sent out the same day.
Helpful Links




As the Uranium atom decays and goes through its half-life it’s converted to Radium-226, which again decays and goes through its half-life, and is converted to Radium-222.
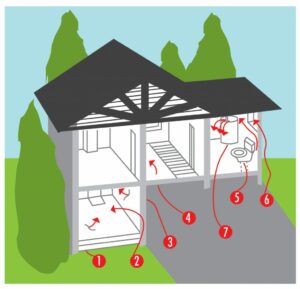
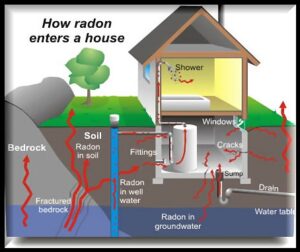
As these conversions take place, the atoms are rising through limestone, bedrock, clay, and soil from hundreds of feet below grade. These atoms eventually surface and can enter homes through cracks on concrete slab floors, cracks in foundation walls, any floor or wall penetrations, windows, well water, etc.
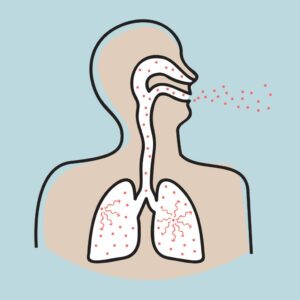
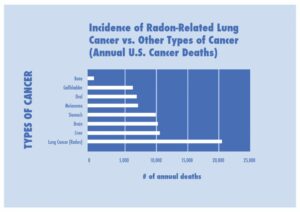
Radium-222 once inhaled decays into radioactive particles that can get trapped in your lungs when you breathe. As they break down further, these particles release small bursts of energy. This can damage lung tissue and lead to lung cancer over the course of your lifetime. Not everyone exposed to elevated levels of radon will develop lung cancer, and the amount of time between exposure and the onset of the disease may be many years.
Radon is measured in pCi/L (picocuries per liter). Picocurie per liter (pCi/L): a unit of radioactivity corresponding to an average of one decay every 27 seconds in a volume of one liter, or 0.037 decays per second a liter of air or water: 1 pCi/L = 37 becquerels per cubic meter (Bq/m3).
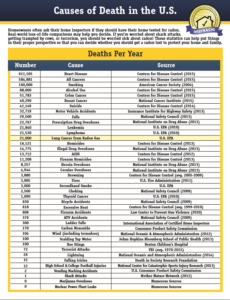
The EPA states any home testing over 4 pCi/L should have a Radon Mitigation system installed to lower Radon levels. I typically find that 1 out of every 3 homes that I test have a Radon level in excess of 4.0 pci/l.